Carbon Footprints of Sugar Factories
- Aug 2, 2024
- 10 min read
Updated: Dec 4, 2024
Sugar, a staple ingredient in many of our favorite foods and drinks, has a rich history that spans centuries. From ancient civilizations to modern-day industries, Sugar Factory Carbon Footprint sugar production has been a cornerstone of agriculture and commerce. Yet, behind the sweetness of sugar lies a pressing issue the carbon footprint of sugar factories. As the world grapples with climate change and environmental degradation, understanding the carbon footprints of sugar production becomes crucial for developing more sustainable practices. In this blog, we will delve into the environmental impact of sugar factories, explore the factors contributing to their carbon footprints, and discuss potential pathways to reduce these impacts.
Yet, behind the sweetness lies a significant environmental challenge Carbon Reduction in Sugar Processing the carbon footprint of sugar factories. Energy Efficiency in Sugar Factories These industrial facilities play a crucial role in sugar production, but their operations have notable impacts on greenhouse gas emissions and environmental sustainability. In this article, we’ll explore what constitutes the carbon footprint of sugar factories, the main sources of these emissions, and strategies for mitigating their environmental impact.
The Sugar Industry A Sweet History with a Sour Impact:
The journey of sugar from field to table is complex and energy-intensive. Sugar production involves several stages, each contributing to the industry’s carbon footprint.
a. Cultivation:
Sugarcane, the primary source of sugar in many regions, requires significant resources. It needs ample water, fertilizers, and pesticides, all of which contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. Sustainable Practices in Sugar Industry Fertilizer production alone is energy-intensive, with the application of nitrogen fertilizers releasing nitrous oxide, a potent greenhouse gas.
The cultivation phase alone can have significant environmental impacts, including greenhouse gas emissions from fertilizer production and pesticide application.
b. Harvesting and Transport:
Once harvested, sugarcane is transported to factories for processing. The machinery used for harvesting and transporting the cane emits carbon dioxide (CO2) and other pollutants. Additionally, the energy used for transportation often provided by fossil fuels adds to the carbon footprint.
This stage involves heavy machinery and transportation, both of which contribute to emissions.
c. Processing:
The processing of sugarcane into refined sugar involves multiple steps: washing, crushing, boiling, and crystallizing. Each of these steps consumes large amounts of energy, primarily sourced from fossil fuels in many regions. Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Sugar Production The burning of fossil fuels releases CO2, further contributing to the carbon footprint of sugar production.
Each of these steps consumes large amounts of energy, often derived from fossil fuels, contributing significantly to the carbon footprint.
d. Waste Management:
Sugar production generates various types of waste, including bagasse (the fibrous residue left after juice extraction), molasses, and sludge. Waste Management in Sugar Factories Managing these wastes often involves additional energy and emissions, particularly if they are not utilized efficiently.
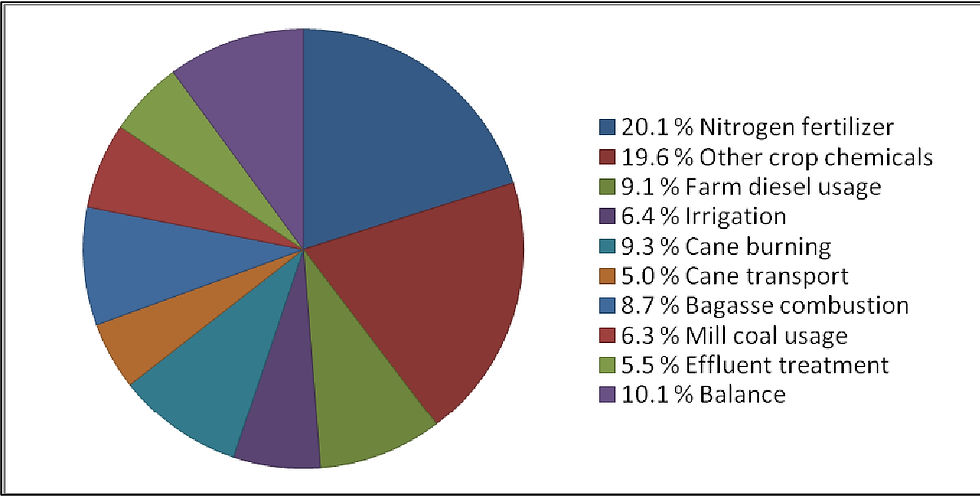
2. Key Contributors to the Carbon Footprint of Sugar Factories:
Several factors contribute to the carbon footprint of sugar factories, each adding layers of complexity to the environmental impact:
a. Energy Consumption:
The most significant contributor to the carbon footprint is the energy used in processing. Many sugar factories rely on fossil fuels such as coal and natural gas to power their operations. This not only contributes to CO2 emissions but also to other pollutants that can harm the environment and human health.
b. Inefficient Practices:
In some regions, outdated and inefficient technologies are still in use. These older methods often require more energy and produce more emissions compared to modern, more efficient technologies. Inefficient boilers, outdated equipment, and poorly managed energy systems all contribute to a higher carbon footprint.
c. Transportation and Logistics:
Transporting sugarcane from the fields to the factories and then distributing the final product involves considerable emissions. Trucks, trains, and ships powered by fossil fuels contribute to the overall carbon footprint.Environmental Benefits of Sustainable Sugar Production Efficient logistics and transportation management are essential to minimizing this impact.
d. Waste Management Practices:
How a sugar factory handles its waste plays a significant role in its carbon footprint. Factories that fail to recycle or utilize by-products effectively may resort to Sugar Production disposal methods that generate additional emissions. Conversely, factories that implement waste-to-energy technologies or use by-products as animal feed can significantly reduce their carbon footprint.
3. The Environmental Impact Beyond Carbon Footprints:
While carbon footprints are a crucial aspect of the environmental impact of sugar factories, there are other factors to consider:
a. Water Usage:
Sugarcane cultivation and processing require substantial amounts of water. This can lead to water scarcity in regions where water resources are already under stress. Renewable Energy Energy Use in Sugar Factories The withdrawal and pollution of water can have severe consequences for local ecosystems and communities.
b. Land Use:
The expansion of sugarcane plantations can lead to deforestation and habitat destruction. Converting forests or natural landscapes into sugarcane fields not only increases greenhouse gas emissions but also threatens biodiversity and disrupts local ecosystems.
c. Air Quality:
In addition to CO2, sugar factories emit other pollutants, such as particulate matter and sulfur dioxide. These emissions can deteriorate air quality, posing risks to both the environment and human health.
4. Moving Towards Sustainability: Solutions and Innovations:
Addressing the carbon footprint of sugar factories requires a multi-faceted approach. Climate Impact of Sugar Production Here are some strategies and innovations that can help reduce environmental impacts.

a. Transitioning to Renewable Energy:
One of the most effective ways to reduce the carbon footprint is by shifting from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources. Solar, wind, and bioenergy can power sugar factories with minimal emissions. For instance, some sugar mills use bagasse as a biofuel, Life Cycle Analysis which can significantly lower their reliance on fossil fuels and reduce their carbon footprint.
b. Improving Energy Efficiency:
Upgrading to modern, energy-efficient technologies can help sugar factories reduce their energy consumption. Energy-efficient boilers, advanced heat recovery systems, Energy Use in Sugar Factories and modern processing equipment can all contribute to a more sustainable operation.
c. Enhancing Waste Management:
Implementing effective waste management practices is crucial for minimizing environmental impact. Factories can explore options such as waste-to-energy technologies, composting, and recycling of by-products. For example, bagasse can be used as a fuel for generating electricity, reducing waste and emissions.
d. Sustainable Agricultural Practices:
Sustainable farming practices can reduce the carbon footprint of sugarcane cultivation. These practices include using organic fertilizers, implementing efficient irrigation systems, and adopting conservation tillage. Integrated pest management and crop rotation can also minimize Greenhouse Gases the need for chemical inputs and improve soil health.
e. Reducing Transportation Emissions:
Optimizing transportation and logistics can help cut down on emissions. This includes improving vehicle efficiency, using alternative fuels, and optimizing routes to reduce travel distances. In some cases, rail transport may be a more sustainable option compared to road transport.
f. Supporting Certification and Standards:
Adopting sustainability certifications and standards can drive environmental improvements. Certifications like Fair Trade and Rainforest Alliance promote sustainable practices in sugar production and encourage factories to adhere to environmental standards.
a. The Thai Sugar Industry:
In Thailand, several sugar mills have adopted renewable energy sources, such as biomass and solar power. Carbon Footprint of Sugarcane Processing Carbon Neutrality These initiatives have significantly reduced the carbon footprint of their operations and set an example for other industries.
b. The Brazilian Ethanol Industry:
Brazil’s sugarcane ethanol industry has made substantial progress in sustainability. By using bagasse as a biofuel and implementing energy-efficient technologies, Brazilian sugar mills have achieved lower carbon emissions and increased energy efficiency.
c. The Indian Sugar Sector:
In India, some sugar factories are focusing on improving waste management and energy efficiency. By utilizing bagasse for electricity generation and adopting modern technologies, these factories are reducing their carbon footprints and improving sustainability.
The world's love affair with sugar is well-documented. We consume it in our daily cups of coffee, add it to our breakfast cereals, and indulge in sweet treats. Sugar Industry Carbon Emissions However, the production of sugar has a significant impact on the environment. Sugar factories, in particular, have a substantial carbon footprint that contributes to climate change and other environmental issues.
The Carbon Footprint of Sugar Production:
Sugar production involves several stages, from planting and harvesting sugarcane or sugar beets to processing and refining. Each stage requires energy, water, and other resources, which contributes to greenhouse gas emissions. Sugar Production Here are some of the key areas where sugar factories have a significant carbon footprint.
Sugar production requires a significant amount of energy to power factories, transport raw materials, and operate machinery. Environmental Benefits of Sustainable Sugar Production The majority of this energy comes from fossil fuels, which releases large amounts of CO2 into the atmosphere.
2.Water Usage:
Sugarcane and sugar beets require large amounts of water for irrigation and processing. This water usage puts pressure on already Climate Impact of Sugar Production scarce water resources, particularly in areas where droughts are common.
3.Fertilizers and Pesticides:
Sugarcane and sugar beets require fertilizers and pesticides to promote growth and protect against pests. These chemicals can leach into waterways, Carbon Neutrality contaminating ecosystems and contributing to eutrophication.
4.Waste Generation:
Sugar production generates significant amounts of waste, including bagasse (the fibrous residue left over after juice extraction), molasses, and other by-products. Improper disposal of these waste materials can lead to environmental pollution.

The Impact of Sugar Factory Carbon Footprints:
1.Climate Change: Greenhouse gas emissions from sugar production contribute to climate change, which has devastating effects on ecosystems, weather patterns, and human societies.
2.Water Pollution: The use of fertilizers, pesticides, and other chemicals in sugar production contaminates waterways, harming aquatic life and human health.
3.Soil Degradation: Intensive farming practices can lead to soil erosion, Industrial Processes salinization, and nutrient depletion, reducing the long-term productivity of land.
4.Loss of Biodiversity: Sugarcane monoculture can lead to the loss of biodiversity, as natural habitats are cleared for cultivation.
Sustainable Solutions for Sugar Factories:
While the carbon footprint of sugar factories is significant, there are steps being taken to reduce its impact:
1.Renewable Energy: Many sugar factories are transitioning to renewable energy Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Sugar Production sources like solar, wind, or biomass power.
2.Efficient Irrigation Systems: Modern irrigation systems minimize Waste Management water waste and reduce the need for fertilizers and pesticides.
3.Organic Farming Practices: Some sugar producers are adopting organic farming methods that reduce the use of chemical pesticides and fertilizers.
4.Recycling and Waste Reduction: Many factories are implementing recycling programs to minimize waste generation and reduce the environmental impact of their operations.
Benefits of Measuring and Managing Carbon Footprints of Sugar Factories:
Understanding and managing the carbon footprint of sugar factories might initially seem like a daunting task, but it brings a host of significant benefits. By measuring and addressing the environmental impact of their operations, sugar factories can not only contribute to global sustainability goals but also enjoy various advantages that enhance their business operations and reputation. Here’s a closer look at the benefits of focusing on the carbon footprints of sugar factories.
1. Environmental Impact Reduction:
a. Mitigating Climate Change
One of the most direct benefits of managing carbon footprints is the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. By implementing strategies to lower carbon emissions, sugar factories contribute to mitigating climate change. This can involve transitioning to renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, and adopting sustainable agricultural practices.
b. Protecting Ecosystems
Reducing carbon footprints helps in minimizing the broader environmental impacts associated with sugar production, such as deforestation, water depletion, and air pollution. This not only protects local ecosystems but also supports biodiversity by preserving natural habitats and reducing pollutants.
2. Economic Advantages:
a. Cost Savings
Managing and reducing carbon footprints can lead to significant cost savings. Energy-efficient technologies and renewable energy sources often result in lower energy bills. Additionally, efficient waste management practices, such as converting Carbon Emissions by-products into bioenergy, can reduce disposal costs and create new revenue streams.
b. Enhanced Operational Efficiency:
Investing in modern technologies and improving processes can lead to more efficient operations. This not only reduces carbon footprints but also enhances overall productivity. Efficient equipment and optimized processes can reduce waste, Sugar Factory Sustainability Practices improve yield, and streamline operations.
c. Risk Management:
Addressing carbon footprints helps mitigate risks related to regulatory changes and environmental compliance. As governments and organizations increasingly enforce stricter environmental regulations, proactive measures can help factories avoid fines,Climate Change penalties, and operational disruptions.
3. Market and Consumer Benefits
a. Enhanced Brand Reputation:
Consumers and businesses are increasingly concerned about sustainability. By demonstrating a commitment to reducing carbon footprints, sugar factories can enhance their brand reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers. Certifications such as Fair Trade and Rainforest Alliance can further boost credibility and market appeal.

b. Competitive Advantage:
Sustainable practices can provide a competitive edge in the market. Companies that prioritize environmental responsibility often find it easier to attract and retain customers, secure partnerships, and differentiate themselves from competitors. Sustainability can be a powerful marketing tool that resonates with both consumers and business clients.
c. Increased Market Access:
Many retailers and distributors are seeking suppliers that adhere to environmental and sustainability standards. By managing their carbon footprints, sugar factories can gain access to new markets and distribution channels that prioritize sustainability in their sourcing decisions.
4. Regulatory and Compliance Benefits
a. Meeting Legal Requirements:
Many regions have regulations and standards related to carbon emissions and environmental impact. By measuring and managing carbon footprints, sugar factories can ensure compliance with these regulations, avoiding legal issues and potential fines.
b. Access to Incentives:
Governments and organizations often provide incentives, grants, or subsidies for businesses that invest in sustainable practices. By actively managing their carbon Climate Impact of Sugar Production footprints, sugar factories may be eligible for financial support or tax benefits related to environmental initiatives.
5. Long-Term Sustainability and Innovation
a. Driving Innovation:
The pursuit of reducing carbon footprints often leads to innovation. Sugar factories that invest in new technologies and processes to lower emissions may also discover more efficient methods and products. This innovation can drive progress and set industry standards.
b. Future-Proofing Operations:
Addressing carbon footprints is not just about current benefits but also about future sustainability. By adopting practices that reduce emissions and environmental impact, sugar factories position themselves as leaders in sustainability, which can be crucial as global environmental challenges continue to evolve.
c. Building Resilience:
Sustainable practices can help sugar factories build resilience against environmental and market changes. Reducing reliance on fossil fuels and improving resource efficiency can make operations more adaptable to fluctuations in energy prices and resource availability.
6. Community and Social Benefits:
a. Positive Community Impact
Sugar factories that manage their carbon footprints often engage in practices that benefit local communities. This can include reducing pollution, conserving water resources, and supporting local biodiversity. These actions contribute to healthier communities and improve the quality of life for residents.
b. Corporate Social Responsibility:
Managing carbon footprints aligns with broader corporate social responsibility (CSR) goals. By demonstrating environmental stewardship, sugar factories can fulfill their CSR commitments and enhance their relationships with stakeholders, including employees, customers, and local communities.
Conclusion:
The carbon footprint of sugar factories is a significant concern in the quest for a more sustainable future. As the world becomes increasingly aware of environmental issues, the sugar industry must rise to the challenge of reducing its carbon emissions and minimizing its environmental impact.
By transitioning to renewable energy, improving energy efficiency, enhancing waste management practices, and supporting sustainable agricultural methods, sugar factories can make substantial strides towards sustainability. The journey towards reducing carbon footprints is not only about mitigating environmental impact but also about setting a precedent for other industries to follow.
As consumers, we can also play a role by supporting products from companies committed to sustainable practices and advocating for environmental stewardship. The path to a sweeter, more sustainable future is paved with innovation, responsibility, and a shared commitment to protecting our planet.
#CarbonEmissions #SustainableAgriculture #SugarIndustrySustainability #ClimateAction #CarbonNeutral #EcoSugarProduction #GreenManufacturing #SugarIndustryClimate #NetZeroSugar
#SugarSustainability #EnvironmentalImpact #CarbonReduction #LowCarbonFarming #SugarFactorySustainability #SustainableProduction #CleanEnergySugar #EcoFriendlyManufacturing





Comments